In order to obtain optimum fatigue properties, the process time should be adjusted to get a complete treatment. Size of shots should be adapted to wire dimension, pitch and shot peening equipment. Shot peening of the inside of the spring coils is particularly critical.
Interested in this product?
Contact us for further discussions. Our dedicated team is ready to assist you, understand your wire product needs, and answer any queries. Submit your request below.
Product request
Medium fatigue
for applications with medium cyclic fatigue requirements
Alloyed Steel
Good balance between strength and ductility suitable for various applications
Coilability
Consistent surface conditions for high performance in forming process
Product information
Technical specification
Mechanical properties
Chemical composition
Surface conditions
Recommendations
Documents
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| E modulus of elasticity | 206 kN/mm² |
| G modulus of shear | 79.5 kN/mm² |
Steel grades and product standards
| Nearest equivalent product standards | ASTM A1000 A | BS 2803 685A55ND |
| Nearest equivalent steel grades | EN TDSiCr | SIS 142090-05 |
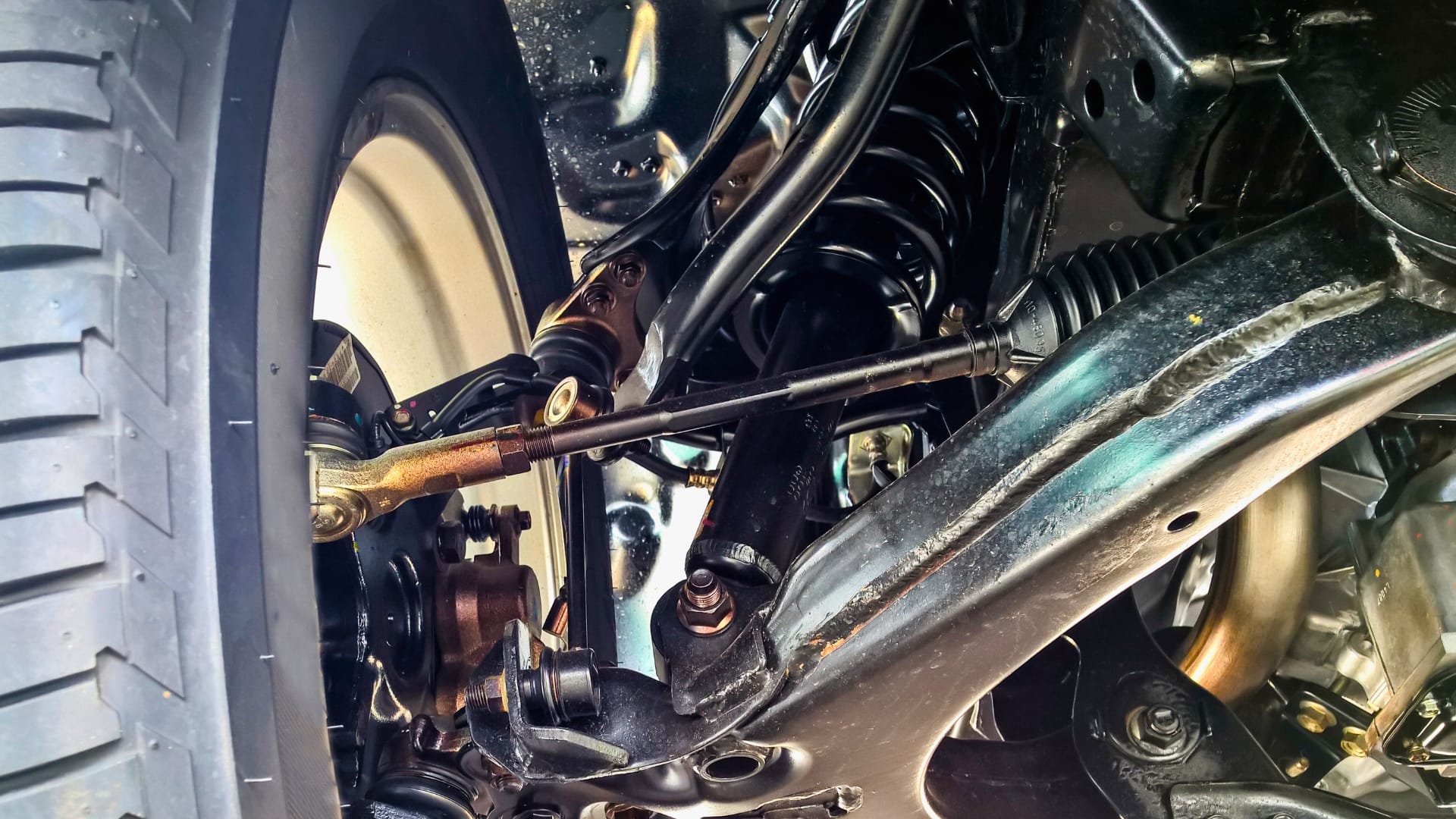
Applications using 70 KD
×
![]()